Would you like us to call you back?
Simply fill out the form below and we’ll be in touch
Would you like to get in touch?
Simply fill out the form below and we’ll be in touch

A Short Guide to Cabling for Power over Ethernet
Date: 17th March 2022
Author: Liz Farrimond
EEE 802.3 have upgraded PoE+ technology to include PoE++. The standard for PoE++ is IEEE 802.3bt and has two classes: type 3 and type 4.
Type 3 uses either 2 or 4 pair copper cable and can deliver up to 51W to a device. Type 4 uses 4 pair copper cable and can deliver up to 71W to a device.
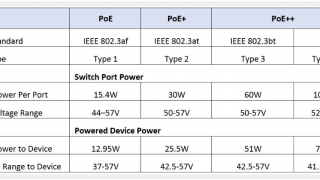
The differences between all PoE types are shown in the table.
A PoE (802.3af) switch provides power for devices that require 15.4W or less. For example, a VOIP telephone or wireless access point. A PoE+ (802.3at) switch provides power for devices that require 25.5W or less. For example, more complex surveillance cameras that pan, tilt, or zoom, wireless access points with six antennas, and video IP phones. A PoE++ (802.3bt) switch provides power for devices requiring up to 51W, using type 3 PoE and up to 71W using type 4 PoE. This would include items such as laptops and TV’s.
The following is applicable to PoE cabling:
• S/FTP cables have better heat dissipation than UTP cables
• AWG22 is more suitable for PoE than AWG24
• Small cable bundles conduct heat better than large ones
• Insulated and enclosed installation spaces (e.g., ducts) hinder heat dissipation
• Only modules certified to IEC 60512-99-001 guarantee the fail-safe operation of PoE applications.
Get in touch to find out how we can help with your next project
Whether you have a technical question, would like a quote or to arrange a site survey, please contact our team.